Data Brokers and Healthcare Medical Records Insurance and Research

In the intricate tapestry of modern society, the exchange of sensitive details about individual well-being has become a pivotal point of discussion. This section delves into the complex interactions between those who facilitate the transfer of such information and the various sectors that rely on it. The focus is on the delicate balance between the utility of this data and the imperative to safeguard the confidentiality of personal health details.
The Role of Information Facilitators in the Health Sector
Information facilitators play a crucial role in the health sector, acting as conduits for the flow of vital details. These entities manage the dissemination of confidential patient files, influence decisions related to coverage, and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge. However, their activities raise significant concerns regarding the protection of individual privacy in the digital age.
The Impact of Information Sharing on Individual Privacy
The sharing of health-related information has profound implications for privacy. As these details are often deeply personal, the manner in which they are handled can either uphold or erode trust in the systems that govern health care. This article explores the challenges and responsibilities associated with the management of such sensitive data, emphasizing the need for stringent safeguards to protect the integrity and confidentiality of personal health information.
Understanding Data Brokers in Healthcare
This section delves into the pivotal role of intermediaries within the healthcare sector, specifically focusing on their involvement in accessing sensitive patient information. These entities facilitate the flow of crucial data, which is essential for various healthcare operations, yet raises significant concerns regarding confidentiality and ethical handling.
Intermediaries in healthcare are often tasked with managing the retrieval of patient histories. This process involves several steps and stakeholders:
- Identification of Necessary Information: Intermediaries must first determine what specific data is required for a particular purpose, such as treatment planning or policy formulation.
- Legal and Ethical Compliance: Ensuring that all data access complies with relevant laws and ethical standards is crucial. This includes obtaining necessary permissions and maintaining transparency with data subjects.
- Data Aggregation: Once permissions are secured, intermediaries aggregate the data from various sources, which might include electronic health records, patient portals, and other healthcare databases.
- Data Processing: The aggregated data is then processed to ensure it is usable and relevant for its intended purpose. This might involve anonymization or pseudonymization to protect patient identities.
- Distribution of Information: Finally, the processed data is distributed to authorized parties, such as healthcare providers, researchers, or insurers, who use it to enhance patient care, conduct studies, or adjust coverage policies.
The role of these intermediaries is critical as they bridge the gap between data availability and data utility. However, their operations must be closely monitored to prevent misuse and ensure that patient confidentiality is upheld. Strategies for oversight include:
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular audits of intermediary practices can help ensure compliance with data protection laws and ethical guidelines.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Implementing robust security measures can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive patient information.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about how their data is used and how they can protect their privacy can empower individuals and foster trust in healthcare systems.
In conclusion, while intermediaries play a vital role in the healthcare sector by facilitating access to patient histories, it is imperative to balance this utility with stringent controls to safeguard personal information. Ongoing efforts to refine regulatory frameworks and enhance data protection practices are essential to maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of healthcare data management.
The Role of Information Intermediaries in Access to Health Records
This section delves into the intricate dynamics between third-party entities and the accessibility of personal health documentation. It explores how these entities facilitate the flow of sensitive information, influencing various aspects of personal and public health management.
In the realm of health coverage, the involvement of intermediaries who specialize in handling vast databases of personal health details is pivotal. These entities play a crucial role in how insurance providers assess risk and determine policy terms. By aggregating and analyzing comprehensive health data, these intermediaries help insurers tailor their offerings to meet market demands and regulatory requirements.
The impact of these intermediaries on insurance policies is multifaceted. On one hand, their data-driven insights enable insurers to offer more personalized and competitive products. This can lead to better coverage options for consumers, potentially reducing costs and opt out whitepages enhancing benefits. On the other hand, the extensive use of personal health data raises concerns about privacy and the potential for discriminatory practices in insurance underwriting.
Moreover, the relationship between these data handlers and insurance companies can influence the transparency and fairness of policy pricing. For instance, if health data is not handled ethically or securely, it could lead to unfair pricing models that disadvantage certain groups of policyholders. This underscores the need for robust regulatory oversight to ensure that the use of health data in insurance practices is both ethical and equitable.
In conclusion, while information intermediaries contribute significantly to the efficiency and innovation in the insurance sector, their practices must be carefully monitored and regulated to protect individual rights and ensure fair market practices. This balance is crucial for maintaining trust in the insurance industry and safeguarding the interests of all stakeholders involved.
Impact of Information Intermediaries on Insurance Policies
This section delves into the significant influence that information intermediaries wield over the realm of insurance policies. These entities, often operating behind the scenes, play a pivotal role in shaping the terms and conditions of insurance offerings, affecting both providers and consumers alike.
Information intermediaries gather and analyze vast amounts of personal data, which is then utilized by insurance companies to assess risk profiles and set premiums. The accuracy and scope of the data collected can significantly impact the pricing and availability of insurance products.
- Enhanced Risk Assessment: By providing detailed profiles of individuals, information intermediaries enable insurers to make more informed decisions about risk, potentially leading to more accurate premium calculations.
- Tailored Insurance Products: The data supplied by these intermediaries can help insurers design more targeted insurance products, catering to specific demographic or behavioral segments.
- Increased Transparency: While beneficial in aiding accurate risk assessment, the use of such data can also lead to increased transparency in the insurance market, as consumers become more aware of how their data is used to determine their insurance rates.
However, the reliance on information intermediaries also raises several ethical and practical concerns:
- Privacy Issues: The collection and use of personal data by these intermediaries can infringe on individual privacy rights, potentially leading to misuse or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Data Accuracy: Inaccuracies in the data provided by intermediaries can lead to unfair insurance practices, where individuals are charged higher premiums based on incorrect information.
- Market Inefficiencies: Over-reliance on data-driven risk assessment can sometimes lead to market inefficiencies, where certain groups are systematically disadvantaged due to biased data analysis.
In conclusion, while information intermediaries offer valuable services to the insurance industry by enhancing risk assessment and product customization, it is crucial to balance these benefits against the potential risks to privacy and fairness in insurance practices. Regulatory frameworks and consumer awareness are essential in ensuring that the use of such data benefits all stakeholders in a just and equitable manner.
Data Brokers' Contribution to Medical Research
This section delves into the significant role that information intermediaries play in advancing scientific inquiry within the medical field. By facilitating access to vast repositories of patient data, these entities enable researchers to conduct studies that could potentially lead to breakthroughs in treatment and care protocols.
The Facilitation of Data Access
Information intermediaries have streamlined the process of accessing comprehensive datasets, which are crucial for conducting extensive medical studies. These datasets often include anonymized patient histories, treatment outcomes, and demographic details, providing a rich source of information for researchers aiming to understand complex medical phenomena.
Enhancing Research Efficiency
By aggregating and organizing data from various sources, information intermediaries help reduce the time and resources required to gather and analyze information. This efficiency allows researchers to focus more on the scientific aspects of their work, accelerating the pace at which new medical insights are discovered.
Ethical Considerations and Data Usage
While the contribution of information intermediaries to medical research is undeniable, it also raises ethical questions regarding the use of personal health information. Ensuring that data is used responsibly and that patient privacy is protected is paramount. Regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines must be continuously updated to reflect the evolving landscape of data usage in medical research.
In conclusion, the role of information intermediaries in medical research is multifaceted, offering both opportunities for advancement and challenges that must be carefully managed. As the field progresses, it is essential to balance the benefits of data access with the need to safeguard individual privacy and uphold ethical standards.
Online Privacy Concerns with Medical Data Sharing
This section delves into the intricate landscape of personal information security within the realm of health data dissemination. As sensitive details are increasingly shared and accessed, the implications for individual privacy become paramount. We explore the mechanisms and regulations that govern these practices, aiming to shed light on the safeguards and potential vulnerabilities in this critical area.
The exchange of health-related data raises significant concerns about privacy and security. This is particularly true when such information is handled by third-party entities. These entities, often referred to as information intermediaries, facilitate the transfer of data between various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, insurers, and research institutions. The following table outlines the primary concerns associated with the sharing of health data:
| Concern | Description |
|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Risk of personal health details being accessed without consent, potentially leading to breaches of confidentiality. |
| Data Misuse | Possibility of health information being used for purposes other than those intended, such as marketing or discriminatory practices. |
| Inadequate Security Measures | Lack of robust security protocols that could prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. |
| Lack of Transparency | Unclear policies regarding how health data is collected, used, and shared, which can lead to confusion and mistrust among individuals. |
Addressing these concerns requires a comprehensive approach that includes stringent regulatory frameworks, advanced security technologies, and transparent practices. It is essential for governing bodies to establish clear guidelines that protect individuals' rights while allowing necessary data sharing for legitimate purposes such as medical advancements and improved healthcare services.
In conclusion, the protection of health data privacy is a complex but crucial issue. As technology advances and the use of health information expands, it is imperative to continually assess and enhance the mechanisms that safeguard this sensitive information. This involves not only technical and legal measures but also fostering a culture of privacy awareness and respect among all stakeholders involved in the handling of health data.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Data Broker Practices
This section delves into the complex landscape of regulations that oversee the activities of entities involved in the collection and dissemination of sensitive personal information. The primary focus is on the legal structures designed to protect individual privacy rights and ensure ethical handling of data. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for both consumers and organizations to navigate the digital age securely.
In the realm of data management, several key regulations play a pivotal role in shaping how information is handled:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This European Union regulation sets stringent standards for the protection of personal data. It impacts any organization that processes data of EU residents, regardless of the organization's location.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Aimed at enhancing privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California, USA, this law grants significant rights to consumers regarding their personal information.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Specifically tailored for the healthcare sector in the United States, HIPAA mandates the protection and confidential handling of health information.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Act: Section 5 of the FTC Act prohibits unfair or deceptive practices in commerce, which can be invoked in cases involving mishandling of personal data.
Each of these regulations imposes specific requirements on entities handling personal data, including:
- Transparency about data collection and usage practices.
- Consent mechanisms that are clear and easily accessible for individuals.
- Security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Accountability mechanisms for data breaches and mishandling.
Implementing these regulatory frameworks effectively requires a combination of technological solutions, policy adherence, and ongoing compliance monitoring. Organizations must not only comply with the letter of the law but also strive to uphold the spirit of these regulations by fostering a culture of privacy and respect for personal information.
In conclusion, the regulatory environment surrounding data management is complex and continually evolving. It is imperative for all stakeholders to stay informed and proactive in their compliance efforts to safeguard personal information and maintain public trust.
Strategies for Protecting Personal Health Information
In this section, we delve into the various methods and practices that individuals and organizations can adopt to safeguard sensitive health data. The focus is on enhancing security measures and ensuring that personal information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
Protecting personal health information (PHI) is crucial in maintaining privacy and preventing misuse. Below are several strategies that can be implemented to enhance the security of PHI:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Utilizing encryption technologies to encode sensitive data, making it unreadable without the correct decryption key. | Prevents unauthorized access even if data is intercepted. |
| Access Controls | Implementing strict access controls to limit who can view or modify PHI. | Reduces the risk of internal data breaches. |
| Regular Audits | Conducting regular audits of data access logs to detect and address any suspicious activities. | Helps in early detection of potential threats. |
| Employee Training | Providing comprehensive training to employees on handling PHI and recognizing phishing attempts. | Enhances awareness and reduces human error. |
| Compliance with Regulations | Adhering to relevant laws and regulations that govern the protection of PHI. | Ensures legal compliance and builds trust with stakeholders. |
Implementing these strategies not only helps in protecting PHI but also in building a robust framework that can adapt to evolving security challenges. It is essential for both individuals and organizations to stay vigilant and proactive in their approach to data protection.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage and Healthcare Privacy
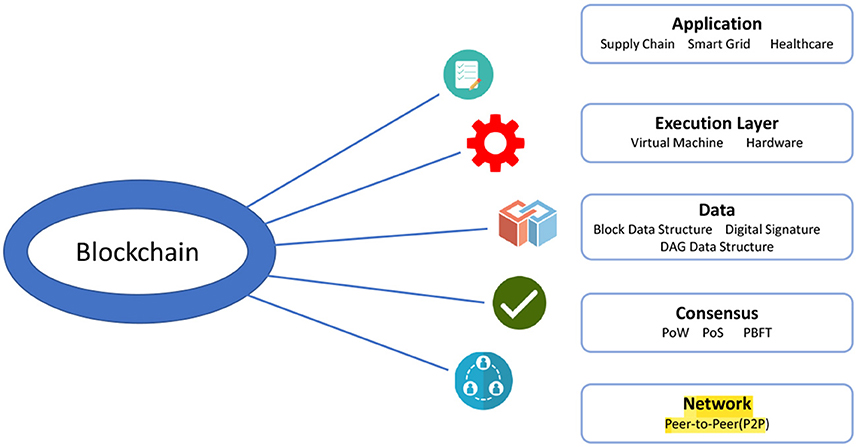
This section delves into the anticipated developments in the realm of information intermediation and safeguarding of personal health details. As technology advances and regulatory landscapes evolve, it is crucial to understand the trajectory of these changes and their implications for maintaining confidentiality and enhancing data usability in the health sector.
The future of information intermediation in the health domain is likely to be shaped by several key trends. These include advancements in data encryption, the rise of blockchain technology for secure transactions, and the implementation of stricter regulatory controls. Below is a table summarizing these trends and their potential impacts:
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Encryption Techniques | Development of more sophisticated methods to protect sensitive information. | Increased security of personal health data, reducing the risk of breaches. |
| Blockchain Integration | Use of blockchain to create a transparent and immutable record of data transactions. | Improved trust and security in data sharing processes. |
| Regulatory Enhancements | Strengthening of laws and regulations governing data handling and privacy. | Greater accountability and compliance among entities handling health information. |
These trends collectively aim to balance the need for data accessibility with the imperative to protect individual privacy. As we move forward, it is essential for stakeholders in the health sector to stay informed and adapt to these evolving practices to ensure ethical and effective use of personal health data.
![]()
